가자미의 개발이야기
[알고리즘] 1. 알고리즘의 효율성, 분석, 차수 본문
알고리즘이란 어떤 문제를 해결할 수 있는 단계 별 절차
Sequential Search Algorithm
//java persue code
public static index SeqSearch(int n, keyType[] S, keyType x){
index location =1;
while(location<=n && S[location] != x)
location ++;
if (location > n)
location = 0;
return location;
}
Binary Search Algorithm
정렬된 상황에서만 가능
//java persue code
public static idex BinSearch(int n, keyType[] S, keyType x){
index location, low, high, mid;
low = 1; high = n; location = 0;
while(low<=high&&location==0){
mid=floor(low+high)/2);
if(x==S[mid])
location = mid;
else if (x<S[mid])
high = mid-1;
else
low = mid +1;
}
return location;
} 배열 크기에 따라 두 알고리즘의 성능차이가 극심해짐.
Sequential = 배열크기
Binary = 배열크기의 차수+1
피보나치 수열이란?
f[0]=0, f[1]=1, ...f[n]=f[n-1]+f[n-2]
Recursive Fibonacci Algorithm 재귀 피보나치 수열
input : int n (>=0)
output : nth term of Fibonacci Sequence
public static int Fib(int n)
{
if(n<=1)
return n;
else
return Fib(n-1)+Fib(n-2);
}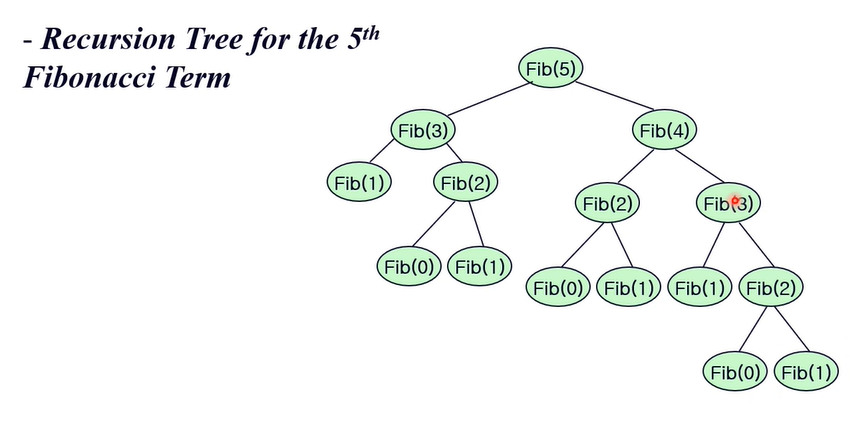
재귀트리로 분석해보면 Fib(3)가 두번 호출되어 비효율적임
짝수인 n을 재귀 피보나치로 구할 때 필요한 트리 개수는 최소 2^(n/2)
Iterative Fibonacci Algorithm 반복 피보나치 수열
input : int n (>=0)
output : nth term of Fibonacci Sequence
public static int Fib2(int n){
index i; int[]f = new int[n+1];
f[0]=0;
if(n>0){
f[1]=1;
for(i=2;i<=n;i++)
f[i]=f[i-1]+f[i-2];
}
return f[n];
}반복 피보나치로 구할 때는 n+1. 효율적.
알고리즘의 복잡도
-input size : 배열 크기, 변수 크기 등...
-basic operation : 알고리즘의 전체 연산량에 큰 영향을 미치는 연산.
시간 복잡도 = 입력크기가 기본연산을 몇번이나 수행하는가.
Every case Analysis : 동일한 입력을 했을 경우 동일한 횟수로 수행
Non-Every case Analysis : 그렇지 않은 경우.
*Best case analysis : 가장 빠른 케이스
*Worst ... : 가장 느린 케이스
*Average ... : 평균적인 케이스
분석할때 세 경우를 고려한다.
이때 n^k으로 복잡도가 나왔을 때, k가 작을 수록 더 효과적이고.
n이 충분히 크지 않은 경우, 기본연산의 영향이 미비하여, 결과가 분석과 다를 수 있다.
'Computer Science > 알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [알고리즘] 대표값 구하기 (0) | 2021.05.16 |
|---|---|
| [알고리즘] K번째 큰 수 (0) | 2021.05.16 |
| [알고리즘] 약수 k번째 약수 구하기 (0) | 2021.05.11 |
| [알고리즘] 약수 k번째 약수 구하기 (0) | 2021.05.09 |
| [알고리즘] 차수 (0) | 2021.03.05 |

