가자미의 개발이야기
[자료구조] 연결리스트로 다항식 구현하기 본문
개념
-다항식을 구성하는 각 항을 노드로 표현
-노드에는 항의 계수와 차수를 데이터로 포함.
-이전에 작성했던 linkedlist.h 와 linkedlist.c를 사용
linkedlist.h(이전에 작성했던 코드에서 노드의 데이터 부분을 약간 수정)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
#ifndef _LINKEDLIST_
#define _LINKEDLIST_
typedef struct ListNodeType
{
int degree;//차수
float coef;//계수
struct ListNodeType* pLink;
}ListNode;
typedef struct LinkedListType {
int currentElementCount;
ListNode headerNode; //데이터가 없는 헤더노드. 연결역할을 한다.
}LinkedList;
LinkedList* createLinkedList();
int addLLElement(LinkedList* pList, int position, ListNode element);
int removeLLElement(LinkedList* pLIst, int position);
ListNode* getLLElement(LinkedList* pList, int position);
void clearLinkedList(LinkedList* pList);
int getLinkedListLength(LinkedList* pList);
void deleteLinkedList(LinkedList* pList);
#endif
#ifndef _COMMON_LIST_DEF_
#define _COMMON_LIST_DEF_
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
#endif
|
cs |
polylist.h
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
#ifndef _POLYLIST_
#define _POLYLIST_
int addPolyNodeLast(LinkedList* pList, float coef, int degree);
LinkedList* PolyAdd(LinkedList* pListA, LinkedList* pListB);
void displayPolyList(LinkedList* pList);
#endif
|
cs |
polylist.c
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
|
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "linkedlist.h"
#include "polylist.h"
int addPolyNodeLast(LinkedList* pList, float coef, int degree)
{
int ret = FALSE, i = 0;
ListNode node = { 0, }; //노드 초기화
node.coef = coef;
node.degree = degree;
if (pList != NULL) {
int length = getLinkedListLength(pList);
ret = addLLElement(pList, length, node);
}
return ret;
}
LinkedList* PolyAdd(LinkedList* pListA, LinkedList* pListB)
{
LinkedList* pReturn = NULL; //다항식 합의 결과 리스트
ListNode* pNodeA = NULL, * pNodeB = NULL; //각 노드에서 순환할 노드
float coefsum = 0;
if (pListA != NULL && pListB != NULL) {
pReturn = createLinkedList(); //결과 리스트 메모리 할당
if (pReturn == NULL) {
printf("메모리 할당 오류, PolyAdd()\n");
return NULL;
}
pNodeA = pListA->headerNode.pLink; //순환할 노드를 첫 원소자리에 둠
pNodeB = pListB->headerNode.pLink;
while (pNodeA != NULL && pNodeB != NULL) {
int degreeA = pNodeA->degree, degreeB = pNodeB->degree; //차수 변수 선언
if (degreeA == degreeB) { //차수가 같을 경우
coefsum = pNodeA->coef + pNodeB->coef;
addPolyNodeLast(pReturn, coefsum, degreeA);
pNodeA = pNodeA->pLink;
pNodeB = pNodeB->pLink;
}
else if (degreeA > degreeB) { //a가 차수가 더 클 경우
coefsum = pNodeA->coef;
addPolyNodeLast(pReturn, coefsum, degreeA);
pNodeA = pNodeA->pLink;
}
else { //b가 차수가 더 클 경우
coefsum = pNodeB->coef;
addPolyNodeLast(pReturn, coefsum, degreeB);
pNodeB = pNodeB->pLink;
}
}
while (pNodeA != NULL) {
coefsum = pNodeA->coef;
addPolyNodeLast(pReturn, coefsum, pNodeA->degree);
pNodeA = pNodeA->pLink;
}
while (pNodeB != NULL) {
coefsum = pNodeB->coef;
addPolyNodeLast(pReturn, coefsum, pNodeB->degree);
pNodeB = pNodeB->pLink;
}
}
else {
printf("오류, NULL 다항식이 전달되었습니다. polyAdd()\n");
}
return pReturn;
}
void displayPolyList(LinkedList* pList) {
int i = 0;
int degreenum = 0;
float coefnum = 0;
if (pList != NULL){
for (i=0;i<pList->currentElementCount;i++){
ListNode *pNode = getLLElement(pList, i);
if (pNode != NULL) {
degreenum = pNode->degree;
coefnum = pNode->coef;
printf("%4.1fX^%d", coefnum, degreenum);
if (pNode->pLink != NULL) {
printf("+");
}
else {
printf("\n");
}
}
}
}
else {
printf("빈 다항식임.");
}
}
|
cs |
example.c
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "linkedlist.h"
#include "polylist.h"
int main()
{
LinkedList* pListA = NULL;
LinkedList* pListB = NULL;
LinkedList* pListC = NULL;
pListA = createLinkedList();
pListB = createLinkedList();
if (pListA != NULL && pListB != NULL) {
addPolyNodeLast(pListA, 6, 6);
addPolyNodeLast(pListA, 4, 5);
addPolyNodeLast(pListA, 2, 2);
displayPolyList(pListA);
addPolyNodeLast(pListB, 1, 5);
addPolyNodeLast(pListB, 2, 4);
addPolyNodeLast(pListB, 3, 2);
displayPolyList(pListB);
pListC = PolyAdd(pListA, pListB);
if (pListC != NULL) {
displayPolyList(pListC);
deleteLinkedList(pListC);
}
}
deleteLinkedList(pListA);
deleteLinkedList(pListB);
return 0;
}
|
cs |
결과
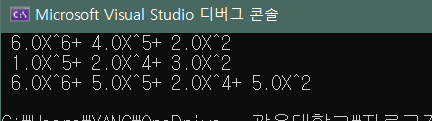
만난 오류들
-LNK 2019 -링크오류, linkedlist.c를 만들지 않고 실행해서 발생. linkedlist.c를 새로 복사해서 만들어줘서 해결
-null pointer 참조 오류, 포인터가 null이 될 수 있는 경우에 참조할 때 발생. 해당 포인터가 null인지 검사해서 해결
'Computer Science > 자료구조' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [자료구조] 배열과 리스트 (0) | 2021.07.05 |
|---|---|
| [자료구조] C언어로 배열 스택 구현하기 (0) | 2021.02.10 |
| C언어로 원형 연결 리스트 만들기 (0) | 2021.02.09 |
| C언어로 링크드리스트(연결리스트) 만들기 (0) | 2021.02.04 |
| C언어로 구현한 리스트 자료구조(ArrayList) (0) | 2021.02.03 |

